NAD+
NAD+ and NADH in brain functions, brain diseases and brain aging
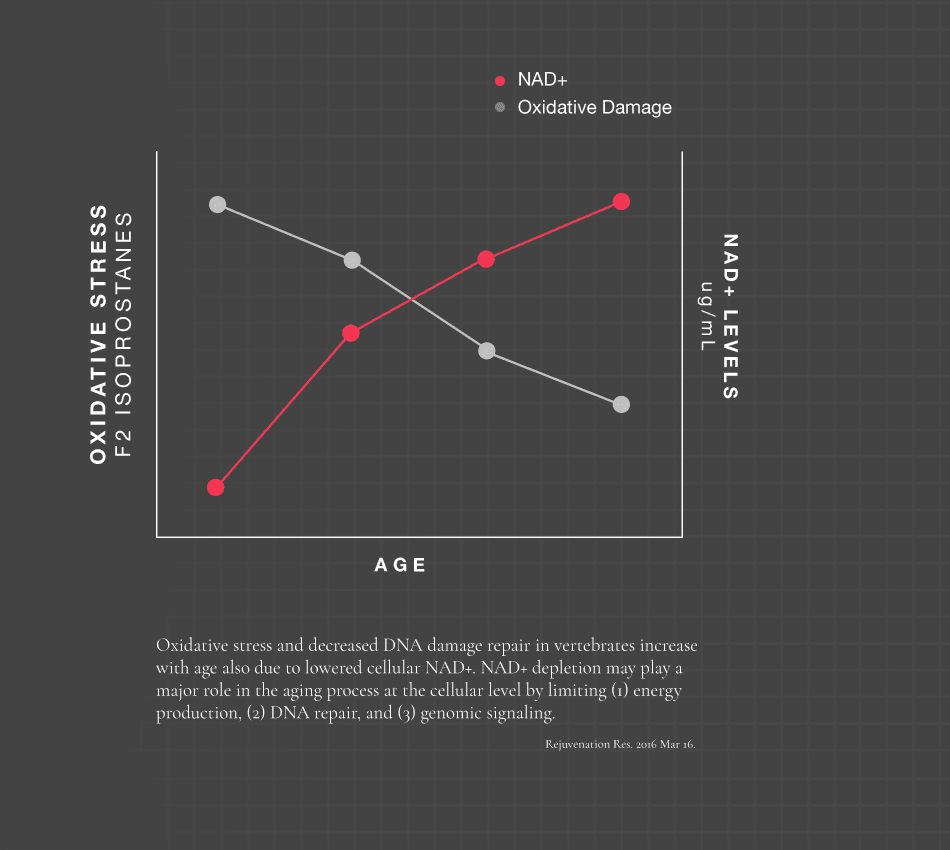
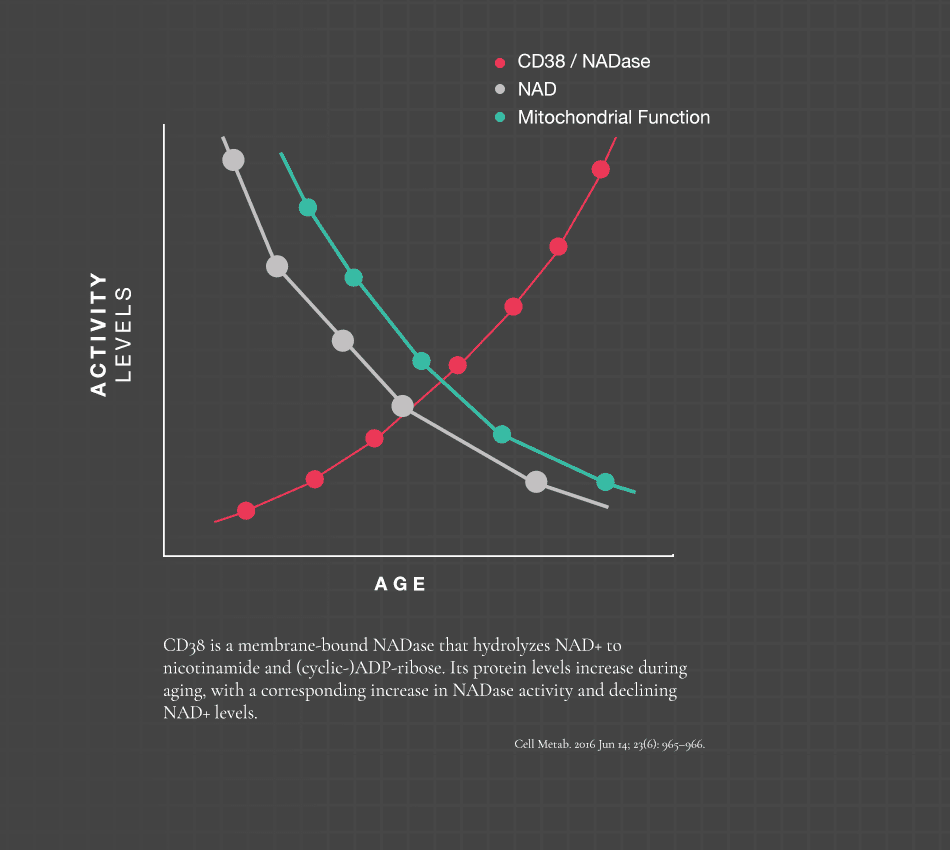
“Numerous studies have suggested that NAD+ and NADH mediate multiple major biological processes, including calcium homeostasis, energy metabolism, mitochondrial functions, cell death and aging. Increasing evidence has also suggested that NAD+ and NADH play important roles in multiple biological processes in brains, such as neurotransmission and learning and memory. NAD+ and NADH may also mediate brain aging and the tissue damage in various brain illnesses. Our latest studies have suggested that NADH can be transported across the plasma membranes of astrocytes, and that NAD+ administration can markedly decrease ischemic brain injury. Based on this information, it is proposed that NAD+ and NADH are fundamental mediators of brain functions, brain senescence and multiple brain diseases.”
Bacopa
Neuropharmacological Review of the Nootropic Herb Bacopa monnieri
“Bacopa monnieri (BM) is traditionally used for various ailments, but is best known as a neural tonic and memory enhancer. Numerous animal and in vitro studies have been conducted, with many evidencing potential medicinal properties. Several randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials have substantiated BM’s nootropic utility in humans. There is also evidence for potential attenuation of dementia, Parkinson’s disease, and epilepsy.”
Cat’s Claw
Cat’s Claw shown to increase Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and improve cognition & focus.
A South American vine with neuroprotective properties, this natural ingredient has been shown to increase brain-derived neurotrophic factor, fight inflammation and free radical damage, repair DNA, alleviate depression, and improve cognition and focus. Research shows that Cat’s Claw has a positive impact on the hippocampus for neurogenesis resulting in improved memory and learning. Cat’s Claw also elevates levels of Tryptophan which increases serotonin and can reduce depressive moods.
CoQ10
Coenzyme Q10 administration increases brain mitochondrial concentrations and exerts neuroprotective effects
“Coenzyme Q10 is an essential cofactor of the electron transport chain as well as a potent free radical scavenger in lipid and mitochondrial membranes. Feeding with coenzyme Q10 increased cerebral cortex concentrations in 12- and 24-month-old rats. These results show that oral administration of coenzyme Q10 increases both brain and brain mitochondrial concentrations. They provide further evidence that coenzyme Q10 can exert neuroprotective effects that might be useful in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.”
Magnesium malate
Enhancement of learning and memory by elevating brain magnesium.
“Our findings suggest that an increase in brain magnesium enhances both short-term synaptic facilitation and long-term potentiation and improves learning and memory functions.”
Thiamin
Thiamin deficiency and brain disorders
“Thiamin plays a key role in the maintenance of brain function. Thiamin diphosphate is cofactor for several enzymes involved in glucose metabolism whereas thiamin triphosphate has distinct properties at the neuronal membrane. Thiamin metabolism in the brain is compartmented between neurons and neighbouring glial cells. Decreased activities of thiamin diphosphate-dependent enzymes (in particular alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase) have also been reported in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases independent of patient malnutrition.”
Glycine
Glycine an important amino acid in supporting cognitive performance and the central nervous system
Glycine is an amino acid that is essential for numerous cognitive and metabolic functions. Glycine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, especially in the spinal cord, brainstem, and retina. Glycine is involved in the transmission of chemical signals in the brain and current research is focussed on its use for mental disorders, schizophrenia, depression, sleep problems, and improving memory.
Aspartic Acid
Aspartic Acid critical in brain and neural health.
Aspartic acid is often connected to mental acuity and keeping the mind sharp. The amino acid is reponsible for increasing concentrations of NADH in the brain and increasing the production of chemicals required for proper mental functioning. Aspartic acid also plays a role in removings toxins from cells including ammonia, which is known to cause damage to the human brain, nervous system, and liver.